How Long Does It Take to Plumbing a New House?
Plumbing a New House
Plumbing work includes any type of installation, repair, or maintenance of pipes and other systems that convey water and waste throughout a building. The system provides freshwater for drinking, cooking, and bathing, and removes sewage and other wastes to prevent overflow and contamination. This is an essential service, and any problems with it can be costly. Understanding how the system works can help you avoid common mistakes that can lead to leaks, flooding, or other serious issues.
The plumbing process is a crucial part of construction, and it can significantly affect the timeline of a project. The exact duration of the work will vary depending on the size and complexity of the building, as well as the number of fixtures that need to be installed. However, there are some general guidelines that can help you estimate the time needed to complete the plumbing for a new building.
In most cases, the plumbing for a new house must comply with the local codes and regulations that govern NYC construction. This means that you will need to submit a plumbing diagram, which details all of the pipes and their sizes. Then, you will need to get a permit from the city’s building inspector. Once the permits are in place, the work can begin.
A key step in the plumbing process is the rough-in phase. During this stage, a plumber locates all of the supply and drain lines, which are usually underground. Then, he or she cuts and joins the pipes to create the necessary connections. Finally, he or she tests the system to ensure that it functions properly and meets all of the local regulations.
How Long Does It Take to Plumbing a New House?
The main plumbing system is composed of two separate subsystems: the freshwater system and the wastewater system. The freshwater system delivers water under pressure to your fixtures, and it also controls the flow of wastewater from those fixtures into the sewer system or septic tank.
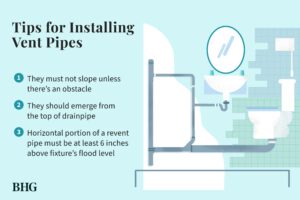
Both of these systems must be properly connected to the DWV system, which is comprised of the main stack, drains, and vents. The main stack is a 3- to 4-inch-diameter pipe that runs from the basement to the roof. Its lowest section collects waste from toilets, and the top portion serves as a vent. All of these pipes must be properly sized and angled to connect to the fixtures and to the DWV system.
In addition, all freshwater and wastewater pipes must be sized appropriately to ensure that they don’t overflow or burst. This is important because overflowing or leaking pipes can lead to serious water damage and health hazards.
The most common types of plumbing fixtures include water closets (also known as toilets), urinals, and bathtubs. Other popular fixtures include sinks, faucets, showers, ice makers, and dishwashers. While most of these fixtures are installed in bathrooms, they can also be found in kitchens, laundry rooms, and other areas of the home.